It is not that every case of flu that is not treated will end up in complications or mortality. Just like any other infection, even if we don’t opt for treatment, our own immune system of our body plays its part in preventing any harm to occur from the invading pathogen.
BODY’S FIGHT WITHOUT ANY AID
Our body’s immune system involves a complex interaction between different pathways to achieve its goal of preventing and curing infection. Serum antibodies, local antibodies, cytokines, interferon, helper T-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, natural killer cells and macrophages are all involved.

These host defense factors stop the shedding of viruses and help in resolution of illness. Virus shedding ceases within 2-5 days from the day of onset of symptoms. Major role is played by interferon, cytotoxic T-cells and natural killer cells.
COMMON MANIFESTATIONS OF FLU
As we know influenza or flu is a disease of respiratory tract caused by influenza virus infection mainly type A and B and it is prevalent in the winter months. It presents as sudden onset fever, cough, and sore throat, watering of eyes, headache and generalized body ache.

The illness begins to resolve in 2-5 days in uncomplicated cases and complete recovery occurs in most cases within a week. In some patients cough may persist for another week after recovery. Weakness is another complaint people complain of after recovery which may persist for sometime even with treatment. That’s why people are advised to bed rest and gradual return to full activity.
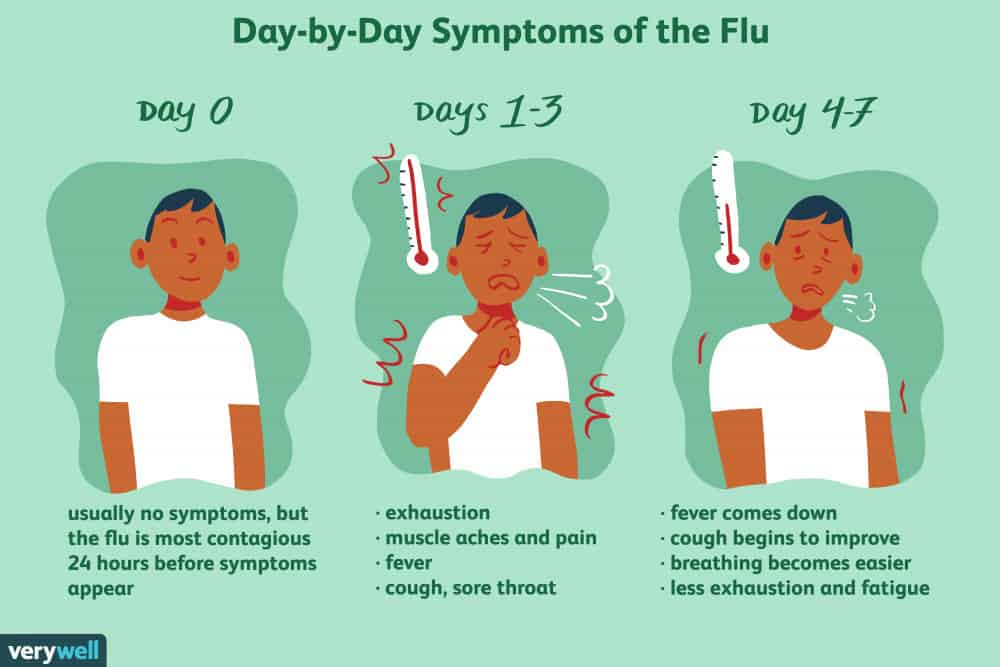
Treatment is effective only if instituted within 48 hours of onset of symptoms. It helps to reduce the duration of illness by a day or two and reduces the chances of complications. Reducing the duration of illness also helps indirectly in cutting the transmission of virus in the community as the infected person remains contagious for a smaller period of time.
COMPLICATIONS WORSENING THE OUTCOME OF THE DISEASE
If the disease is not treated promptly it can have serious multitude of manifestations. These range from pneumonia to multi-organ involvement. Other organs targeted are brain(causes encephalitis, transverse myelitis), musculoskeletal system (myositis,rhabdomyolysis), heart (myocarditis) and kidney (renal failure). All these accentuate the mortality of the patient.
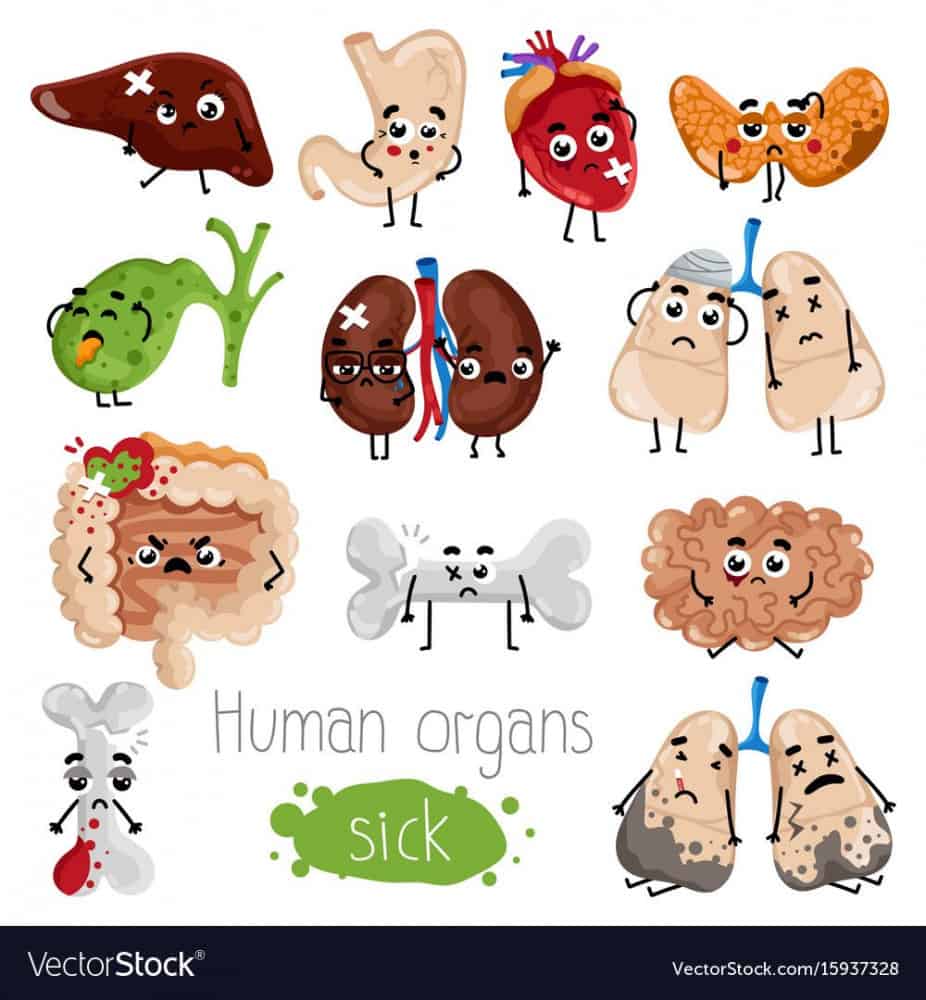
Risk of developing complications is higher in patients who are not treated with specific antiviral drugs like oseltamivir and zanamivir. As a result, mortality rate is also lowered by treating patients. Complicated cases require treatment as they are at much higher risk of dying due to complications. In severely ill patients, ventilator support may be required and unless it is provided they are surely going to lose him.
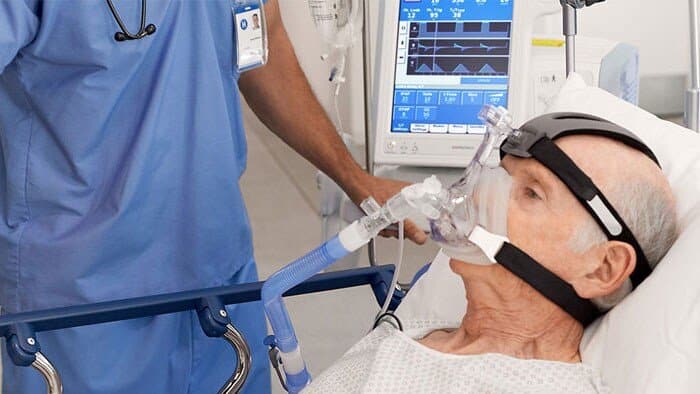
Those who develop bacterial pneumonia as a complication should be provided with antibiotics, otherwise it will end fatally. People also exacerbate their underlying illnesses during the attack of flu and should be treated for those conditions.
It is also important to prevent flu in patients in the high risk category (children, young infants, elderly, pregnant women, health care workers, persons suffering from chronic cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases) as influenza is potentially hazardous.
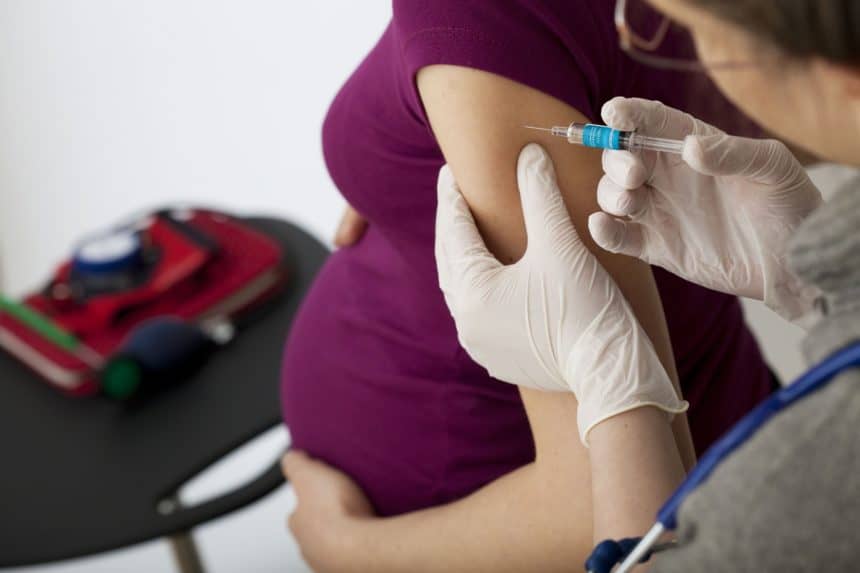
It is always better to get treated for flu at the first sign of it, because you never know, you might be the next person to develop serious complications. Also the benefits of treatment significantly outweigh the cost of the treatment instituted.
LEARN FROM HISTORY
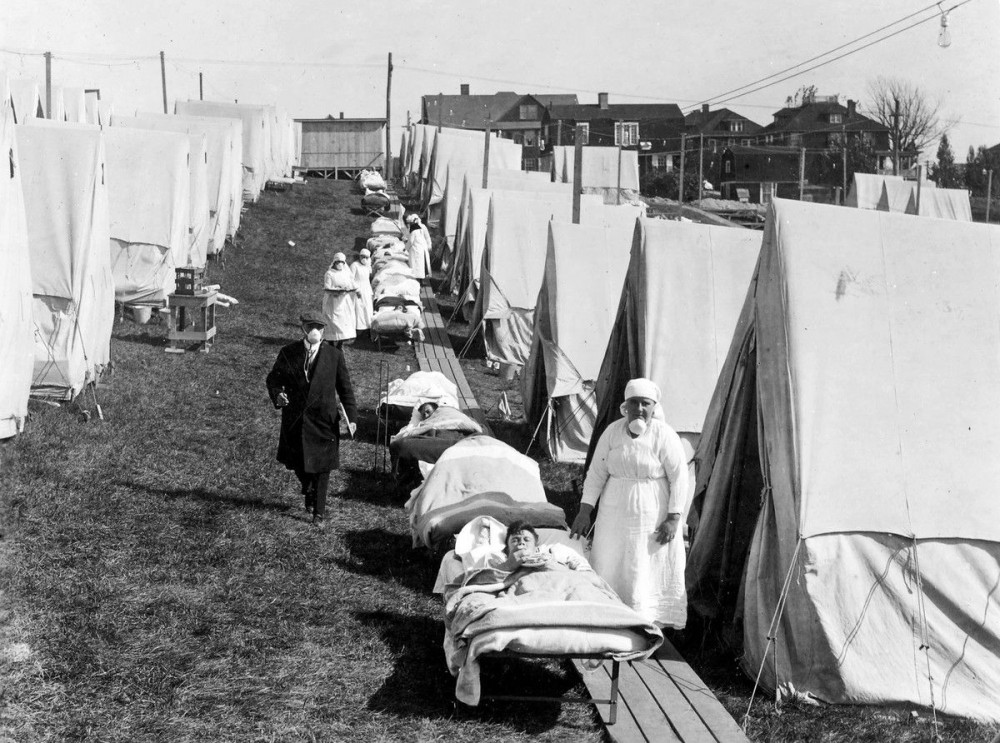

It is said that those who don’t study history properly are bound to suffer from its repetition. The Spanish flu pandemic bears testimonial to the above statement. The global pandemics have played havoc in the past engulfing millions of lives and ruining the economic stability of various countries. So, it need not be emphasized about the need of active steps to be undertaken to prevent potential explosive outbreak of the disease in near future.