Jim Cramer, stock market guru and host of the hugely popular CNBC daily investment program, “Mad Money” when responding to the question of a caller to his show recently put it succinctly when he said, “I really can’t think of a reason when you wouldn’t use a limit order.”
Buy Limit Order Defined
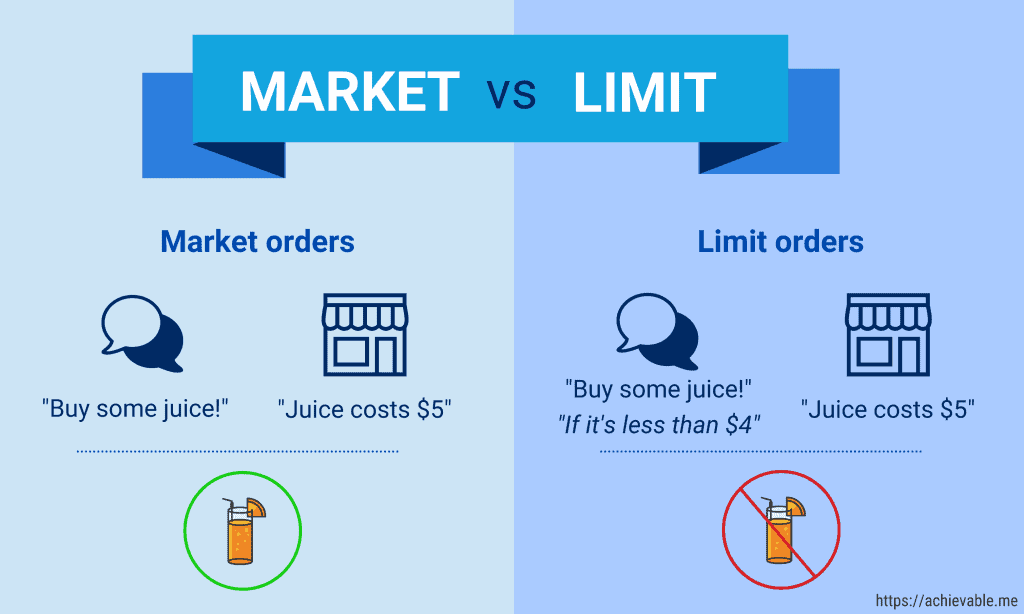
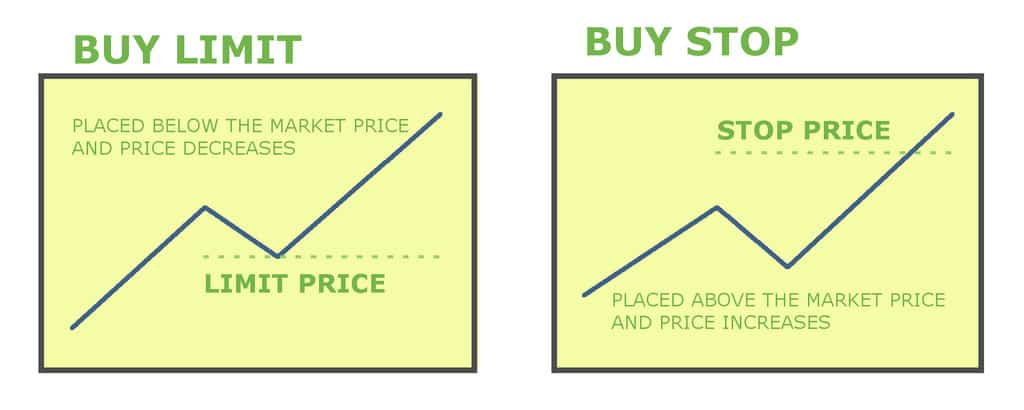
A buy limit order is an order to buy shares of stock at a set or better price.
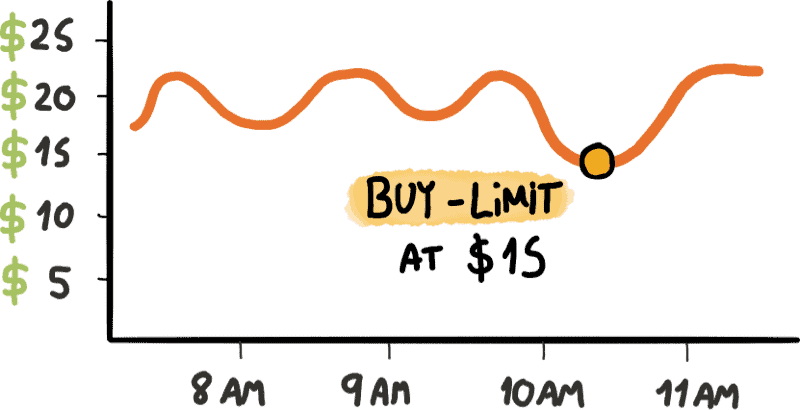
A brokerage order to buy stock placed without conditions, is a termed a market order. Market orders are filled at the market (current) price in effect at the time the order is executed.
Especially when the price of a stock is volatile and the price is moving up and down quickly, using market orders may result in an investor buying a stock during a spike in price only to realize an immediate loss when the price later settles lower. Wise investors never trade at market but use buy limit orders instead.
Thus buy limit orders preclude paying too much for a stock.
Considerations When Using a Limit Order
There is a chance of course that a buy limit order will never be filled if the price of the stock in question does not fall to or below the price specified but that is actually a fairly rare occurrence. Even should that occur, it is difficult to think of a situation where it is a good thing to pay too much for a stock.
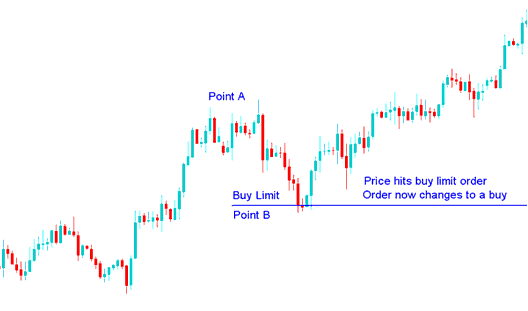
If for example an investor was chasing a hot stock, never a wise idea, and entered a market order when the stock was priced at $37, the price might climb to $44 before the trade is executed. Rarely is it profitable to be caught in that sort of situation.
Given the chance that a buy limit order may not be filled quickly or as mentioned in rare instances not at all, it is also a good practice to specify a time limit as well as a price limit.

Buy orders are “good until canceled” and a buy limit order could conceivably be executed several days or weeks later when an investor may no longer be interested in buying the stock should he forget to cancel the order.
How to Set the Price of a Limit Order
Determining a price for a limit order for the best chance of seeing the order executed is not overly complicated. Investors should obtain a real time, complete quote on the stock being considered. Complete quotations show the ask price ( the lowest price a seller is willing to sell the stock at) and the bid price ( the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for the stock). The difference between bid and ask is termed the “spread.”
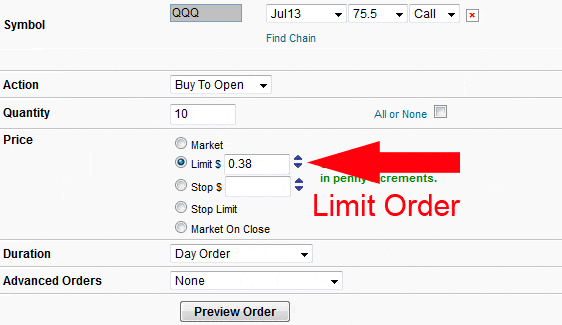
To maximize the chances of having a buy limit order executed and to minimize the chance of paying too much, the investor should specify a price reasonably close to the current asking price for the stock. Setting the specified price too low increases the chance that the trade will never be consummated.
Cost of Buying Stock Using Limit Orders
Some brokers do charge a higher commission for limit orders than market orders. Many discount brokers like Scottrade do not charge more for online limit orders.
Even at the firms that do charge more, the difference is generally a nominal amount and well worth the insurance against buying a stock at too high a price. It is a good idea for investors to check the commission schedule at their broker ahead of time to learn whether limit orders cost more and if so, how much more.
The Least That Should be Known About Buy Limit Orders
- A buy limit order is an order placed with a broker to buy a set number of shares at a specified price or better.
- Buy limit orders also allow investors to limit the length of time an order can be outstanding before being canceled.
- Depending on the brokerage used, commissions on limit orders may be higher than on market orders.
- Limit orders generally do not execute as quickly as market orders.
- A buy limit order will not be executed at all if the market price of the stock does not fall to or below the price specified in the order.
- Maximizing the chances of a limit order being executed requires that the price specified be reasonably set in slight favor of the stock’s asking price.