Erythromycin is an important antibiotic in the macrolide class. That group includes biaxin, E-mycin, EES and zithromycin (zpack), among others. It can be taken by pill, capsule, intravenously, or used topically on the skin or even as eye drops. Pediazole is a combination of erythromycin and a sulfa drug.

What does Erythromycin Treat?
Erythromyocin is used for bacterial infections. Erythromycin (EES, Biaxin, Z-pack) is the number one substitute for those who are allergic to penicillin. It is also safe to use during pregnancy (although not Biaxin). Only a few of the many infections this broad-spectrum antibiotic treats are listed below:
- skin infections including acne
- lung diseases including pneumonia
- sinus infections
- strep throat when allergic to penicillin
- Lyme disease
- pertussis
- pelvic inflammatory disease
Side Effects with Erythromycin Can be Confused with Allergic Reactions
Erythromycin and its common forms with similar names typically cause gastric problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or decreased appetite. These are all side effects and not allergic reactions to mycins.
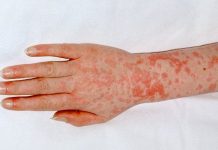
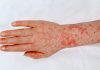
Severe side effects include rashes, changed heart rhythm, swelling of the face, change in hearing, seizures, blistered skin, wheezing and difficulty breathing. Some of these represent true allergy and some indicate a contraindication to using the drug due to extreme discomfort.
Some find decreased side effects when taking Zithromycin or Clarithromycin. If they can take these medications they aren’t allergic to mycins or macrolides.
Side Effects of Erythromycin (macrolides) when Combined with Other Drugs
Interactions don’t mean allergic reactions. Some drugs are not meant to be used with erythromycin and this is usually stated on the drug insert. A reaction to the combination does not mean an allergy to either medication but it does mean the medication shouldn’t be combined in most cases.

- Erythromycin may cause abnormal heartbeats in combination with some medicines such as quinine and some anti-psychotics.
- EES may reduce the effectiveness of birth controls. Another method should be used while taking the antibiotic.
- Erythromycins in combination with statins for cholesterol may increase muscle pain.

- There are increased risks of side effects with anti-fungal and some asthma medications.
- Erythromycin may increase the levels of blood thinners, so this combination needs vigilence.
- Erythromycin also increase the blood levels of digoxin, buspirone, Dilantin, to name a few drugs.
Why it is Important to Understand if it’s a True Allergy to Antibiotic Erythromycin
EES is a very important drug used to fight many types of bacterial infections. To unwittingly claim a false allergy makes the whole drug class useless, thus another class of drugs must be found to treat the infection.
Not only does this introduce more drugs into the battle of antibiotic overuse, but it may cause a mild infection to be over treated and to end up being a stronger infection as it morphs into drug resistance.
Someone might be sensitive to erythromycin but can take Biaxin and Z-packs. Someone else might notice a funny taste after taking Biaxin. These people aren’t allergic to erythromycin. By assuming an allergy to any one of the macrolides, the whole class of antibiotics becomes off limits, thus reducing the options to treat an infection.
With the increased use of electronic records and pharmacy internet availability, a whole class of drugs may become off limits based on a faulty impression of allergy. On the other hand, understanding a true allergy is vital to receiving the correct medication when needed.