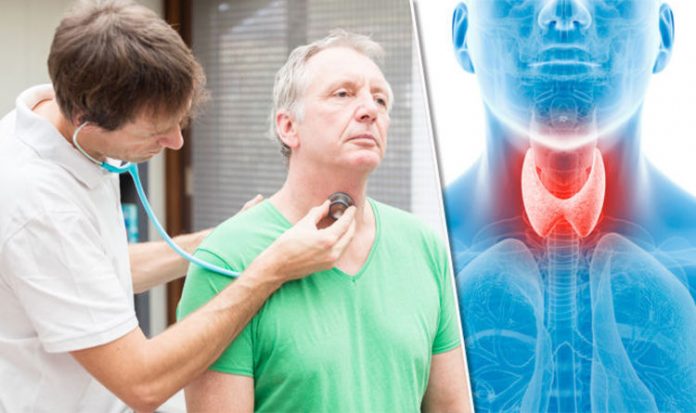
The thyroid is one of the endocrine glands in the human body. It is located in the lower portion of the neck. The function of this gland is to produce thyroid hormones. It does this by using the chemical element called iodine. Iodine gets into the body mostly through ingestion of iodine-rich foods like seafood, bread and ionized salt. According to the American Thyroid Association, the thyroid hormones, thyroid.org “Thyroid Hormone Treatment”) are important in the body’s growth, development and metabolism of cells.
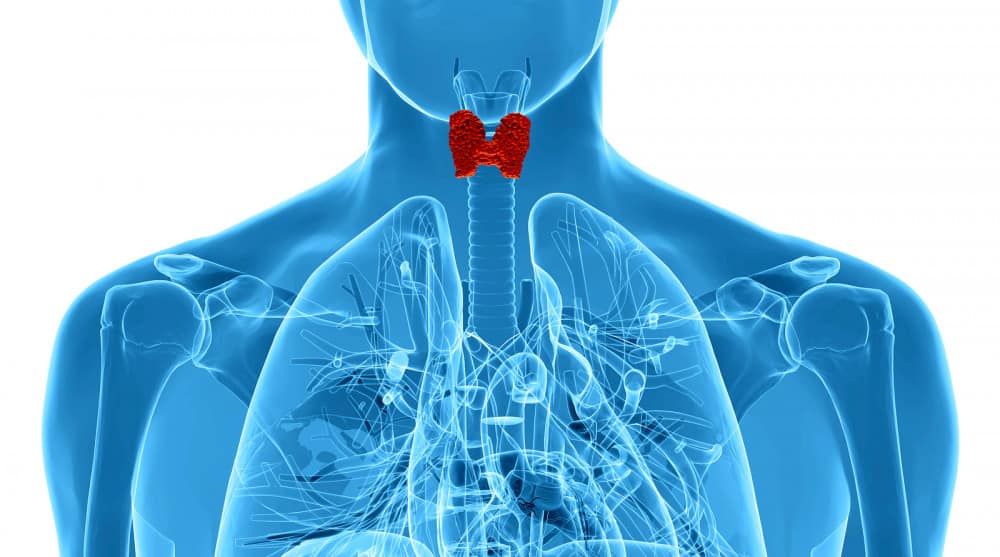
When the thyroid gland does not function correctly, abnormally high (hyperthyroidism) or abnormally low amounts (hypothyroidism) of thyroid hormones are produced. The affects of abnormal levels of thyroid hormones can cause severe physical problems. In most cases, hypothyroidism can easily be treated Webmd.com, “Hypothyroidism-Treatment Overview,”.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
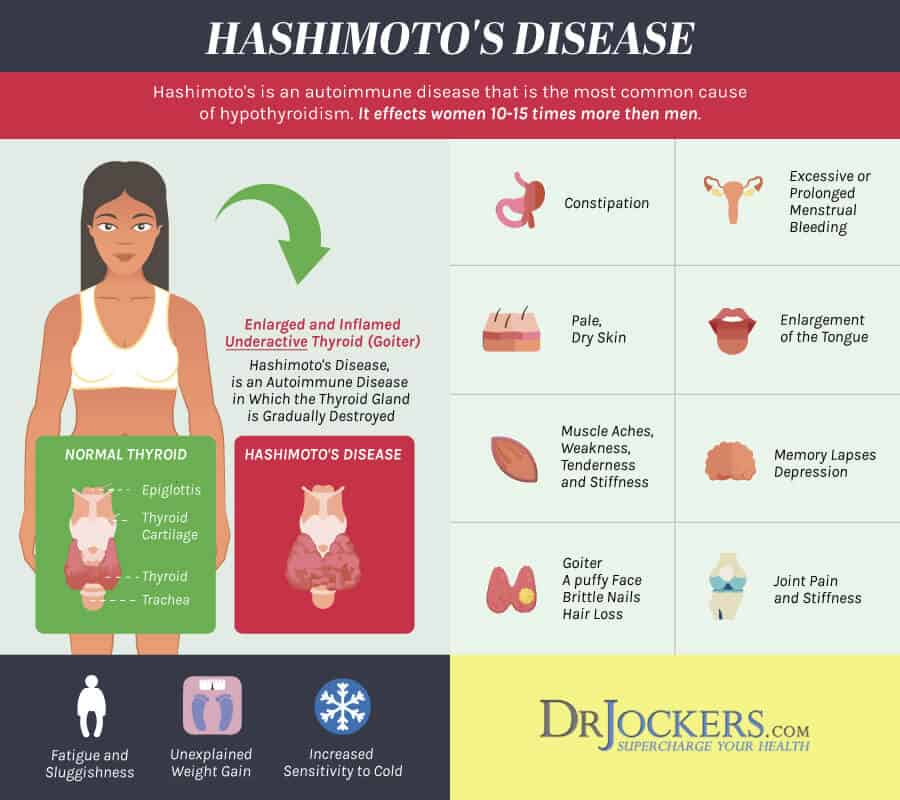
There are many reasons for deficient production of thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism is a common disorder, especially among women and older adults. The incidence of this disorder increases with age. The most common cause of hypothyroidism involves the autoimmune system. This type of hypothyroidism is called Hashimoto Thyroiditis. This occurs when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the tissues of the thyroid gland causing it to enlarge (goiter) and to interfere with its production of hormones.
Another cause of hypothyroidism is a side effect or adverse response to the treatment of hyperthyroidism. Sometimes the treatment for over production of thyroid hormone results in a low functioning thyroid.
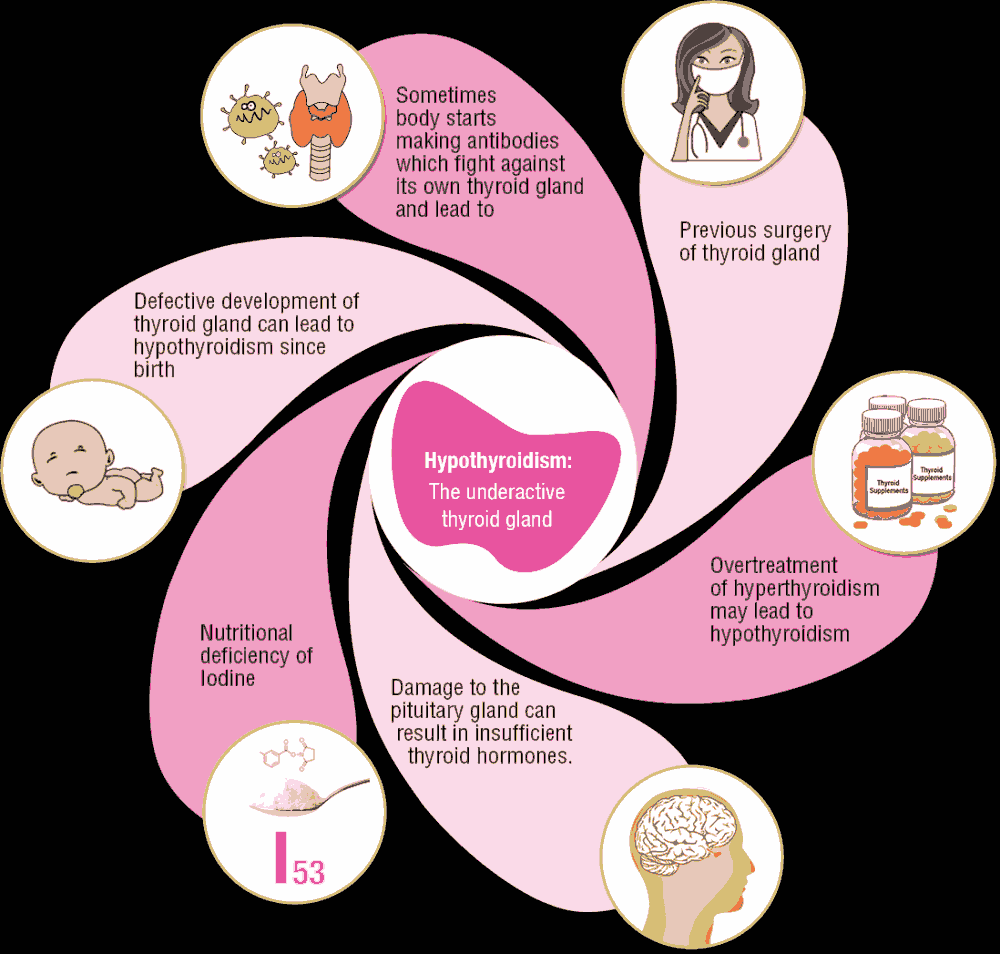
A third cause may be an adverse response to or a side effect of medication therapy. Treatments like radiation and radioactive iodine can cause injury to the thyroid gland causing hypothyroidism.
Surgery to remove the thyroid or to remove even a portion of the thyroid can cause the production of the thyroid hormones to be decreased or to stop completely. A woman can develop hypothyroidism during pregnancy and this disorder can even be congenital. A body that deficient in the chemical element iodine can lead to hypothyroidism.

Another disorder involving another gland can cause hypothyroidism. This gland is the pituitary gland. If the pituitary gland has been injured or does not function correctly, it can directly affect the function of the thyroid gland Mayoclinic.com, “Hypothyroidism-Underactive Thyroid” .
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Many of the symptoms of hypothyroidism are general, non-specific complaints. These complaints can signal a multitude of health problems. Only after specific laboratory blood work results can the diagnosis of hypothyroidism be confirmed. A person can be treated for hypothyroidism due to the symptoms that they present even if their blood has not been tested.
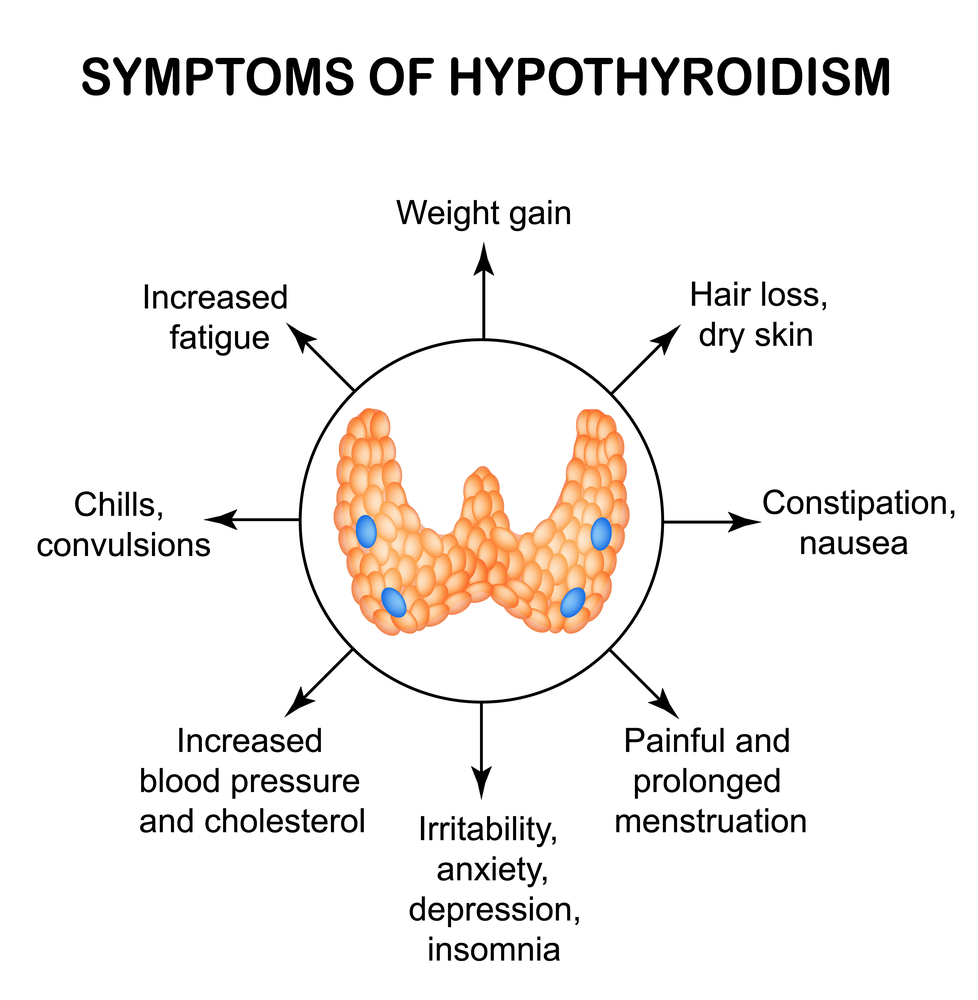
A person whose blood work does not confirm hypothyroidism can still actually have the disorder. These people may go undiagnosed until the condition progresses and their metabolism is slowed. A person can have hypothyroidism and not show symptoms. until the condition progresses and slows metabolism. Hypothyroidism is diagnosed or confirmed through laboratory blood testing.
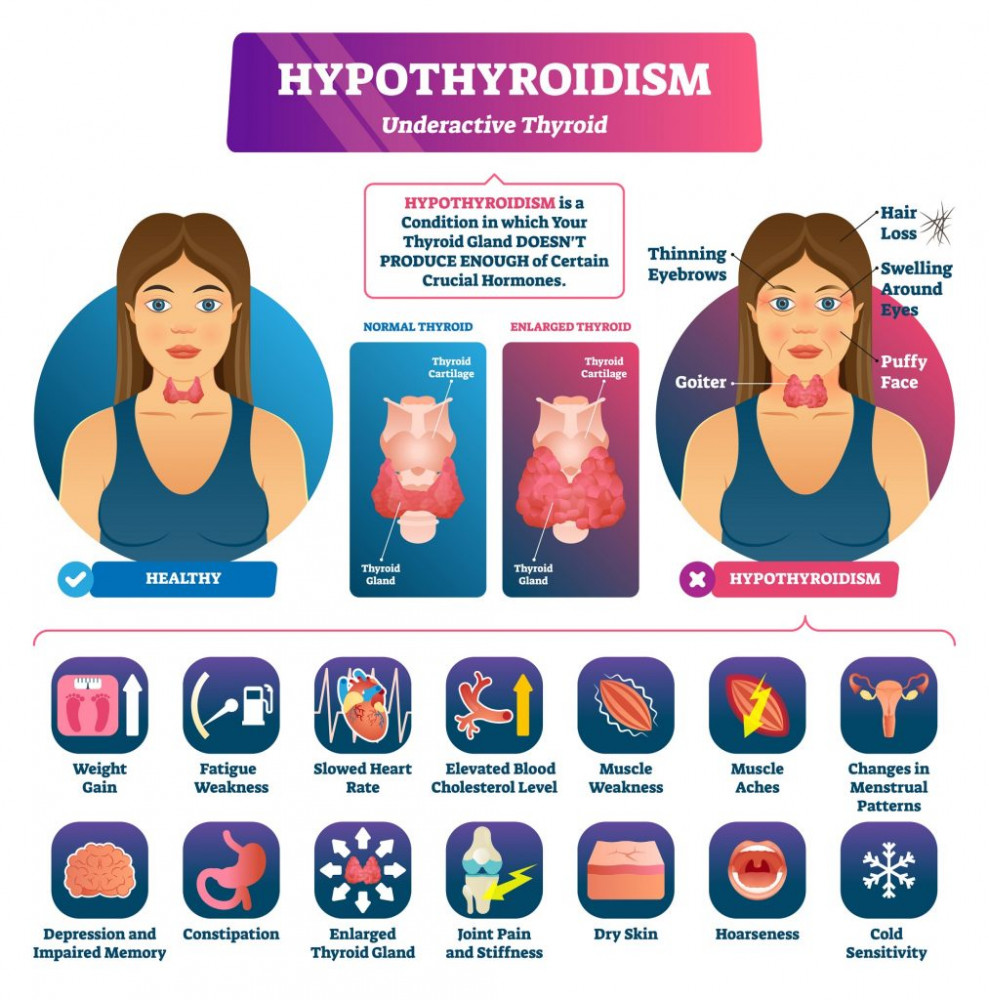
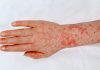
The most common complaints of people with hypothyroidism are generalized weakness and fatigue. Other common symptoms include rapid weight gain, dry skin, flaky skin, dry hair, constipation, muscle cramps and generalized aches and pains. As the disease progresses, symptoms can include depression, intolerance to cold temperatures, swelling in legs, higher cholesterol levels and inability to concentrate.
As hypothyroidism becomes more severe, there may be slowing of the heart rate, a cooler body temperature and swelling around the eyes. In its most critical form, untreated hypothyroidism can lead to severe illness, can lead to coma and can even cause death Webmd.com, “A-to-Z-Guides/Hypothyroidism,”.