Lopressor is a heart medication used to treat hypertension, angina pectoris or chest pain, glaucoma, migraines, ventricular arrhythmias and to prevent miocardial infarction or heart attacks. It is classified pharmacologically as a beta blocker. It also falls under the classification of antianginal and antihypertensive.

Other beta blockers are:
- atenolol or tenormin
- carvedilol or coreg
- propranolol or inderal LA
- acebutolol or sectral

How Lopressor Works
The heart contains beta1 adrenergic receptors. These receptors stimulate the heart to beat faster and increase blood pressure when they are stimulated. Beta blockers like lopressor block stimulation of these cells and in the process reduce blood pressure and the rate at which the heart beats.
Lopressor does not usually affect parts of the body that have beta2 adrenergic receptors like the lungs and uterus.
Before Taking Lopressor
Some people should not take lopressor if they suffer from certain diseases such as:
- uncompensated congestive heart failure
- pulmonary edema
- shock originating from the heart or cardiogenic shock
- low heart rate
People who have respiratory diseases like asthma should take lopressor with caution because at higher doses, it may affect the beta2 receptors in the lungs and cause constriction of the airways making it difficult for the person to breathe. Kidney and liver problems may require that a person take this medication with caution.
Lopressor may interact with other drugs in the following ways:
- low heart rate may occur when lopressor is taken with digoxin
- low blood pressure may occur when lopressor is taken with other antihypertensive medications
- lopressor may change the efficacy of insulins or oral hypoglycemic drugs
Side Effects of Lopressor
Some side effects of lopressor are:
- dizziness
- fatigue
- depression
- drowsiness
- nausea
- vomiting
- constipation
- diarrhea
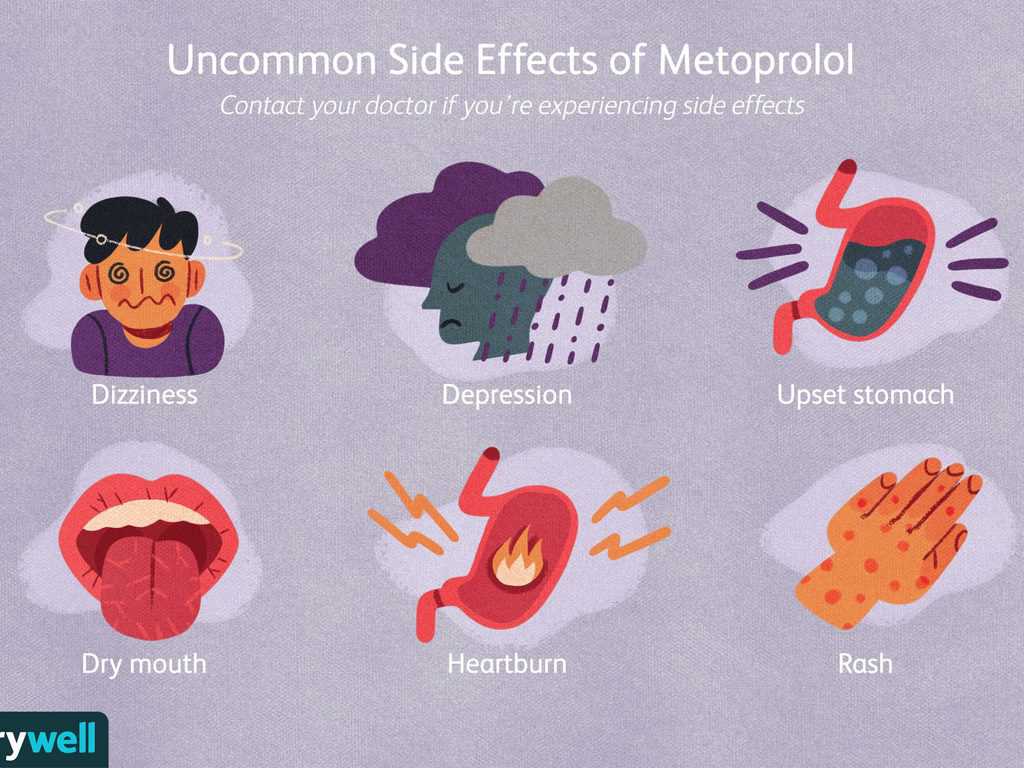
- heartburn
- dry mouth
- flatulence
- stuffy nose
- stomach ache or pain
Adverse effects of lopressor are severe effects that need to be reported to a physician immediately.
Some of them are:
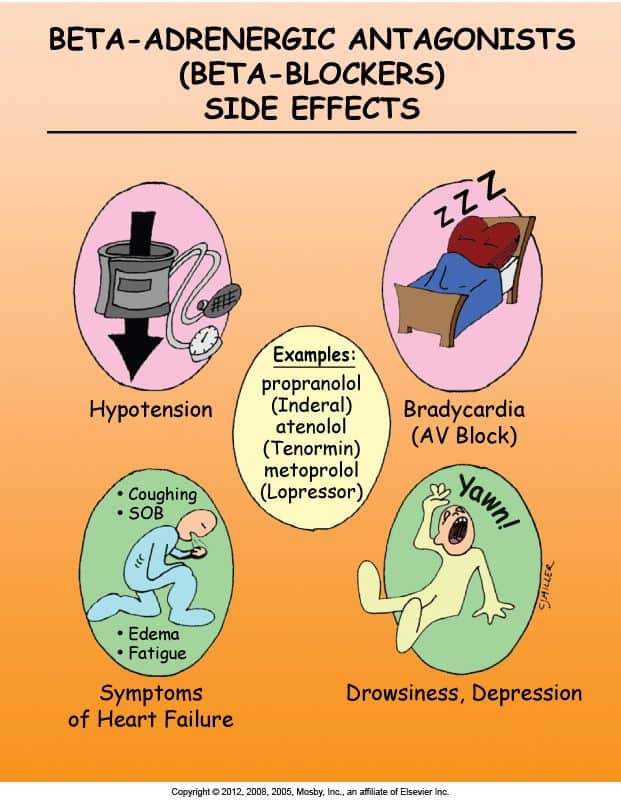
- wheezing
- difficulty breathing
- fainting
- rapid heart beats
- irregular heart beats
Teaching/ Nursing Interventions
The registered nurse teaches the patient with a prescription for lopressor the following:
- not to stop taking the medication abruptly
- how to check blood pressure, pulse and the importance reporting any changes from the normal to a health care provider

- to avoid driving or activities that need alertness until they know how the medication will affect their mental status since lopressor may cause drowsiness
- to get up from a lying or sitting position slowly to avoid falls due to dizziness
- to consult a physician before taking any over the counter medication
- to closely monitor blood sugar levels if the patient is diabetic

- to report any adverse effects of lopressor to a physician along with any bothersome or severe side effects
When taking any medication such as lopressor, it is important to comply with whatever advice a health care provider gives in order to remain in good health. Therefore when taking lopressor or any other medication, it is necessary to express any concerns about the medication to a healthcare provider.