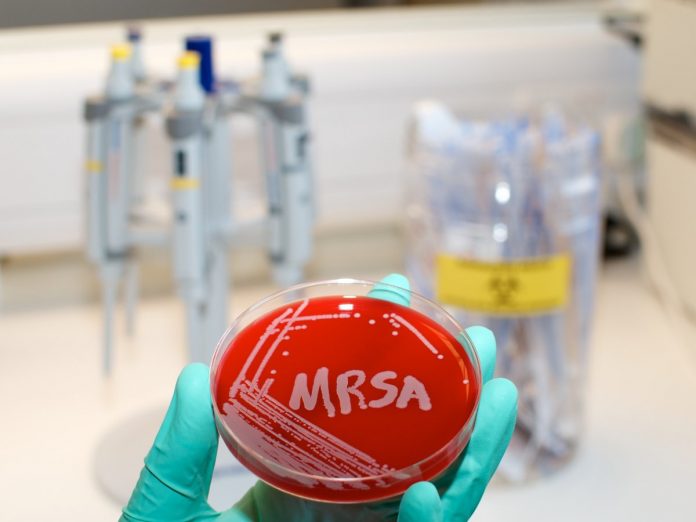
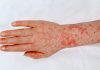
MRSA is another name for a group of bacteria known as methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylococcus aureus is a type of bacteria that’s commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes, but usually doesn’t cause infection unless the immune system isn’t working properly.
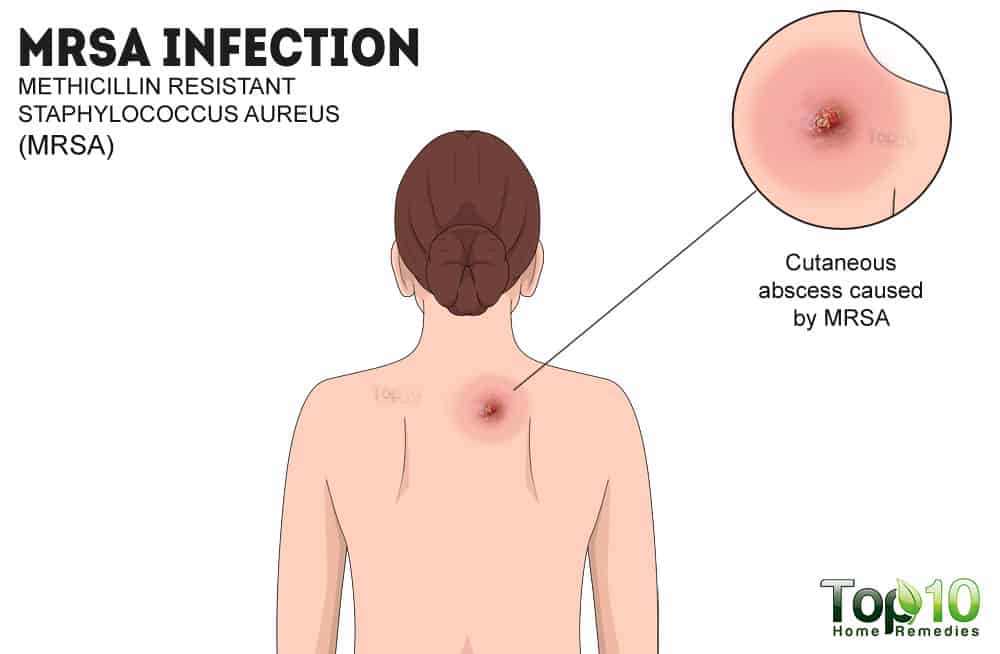
In this case, the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria can invade the body and cause boils or other types of skin problems – and even lead to more serious infections in other areas such as the heart, bloodstream, or bones.
What is MRSA Bacteria?
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria are called MRSA because they’re resistant to most of the antibiotics normally used to treat bacterial infections. This makes treating a MRSA infection difficult since most antibiotics will be ineffective. This makes a MRSA infection far more serious than the average bacterial infection.
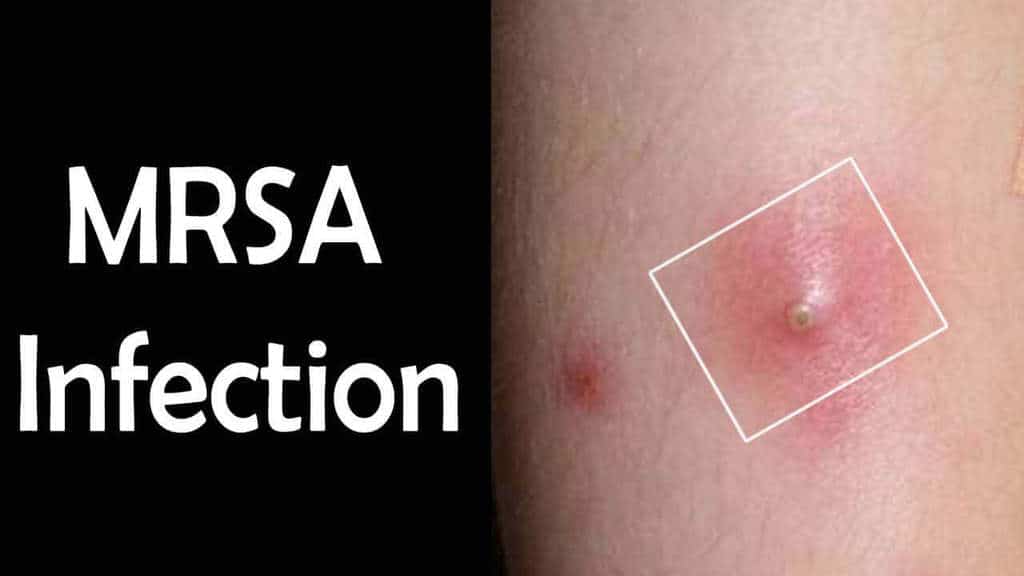
How is MRSA Contracted?
Sometimes people are colonized with MRSA bacteria, but their immune system keeps the bacteria from causing problems – although the bacteria can still be transmitted to others. A person can be exposed to the MRSA bacteria by touching an open wound or by sharing towels or other articles with a person carrying the bacteria.
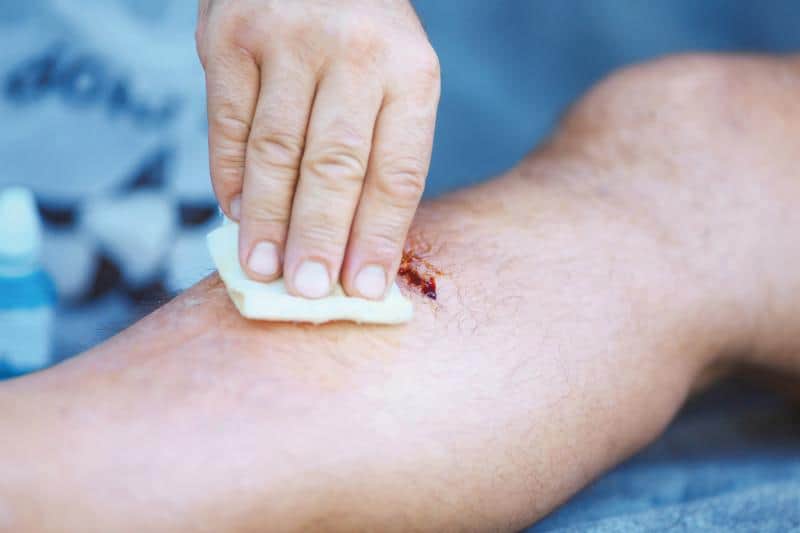
If the person exposed has a cut or open wound, it allows the bacteria to enter the body. Then, if they don’t have a healthy immune system, the bacteria can cause a skin infection or spread to other areas including the bones, bloodstream, and valves of the heart. When this happens, it can be life-threatening.
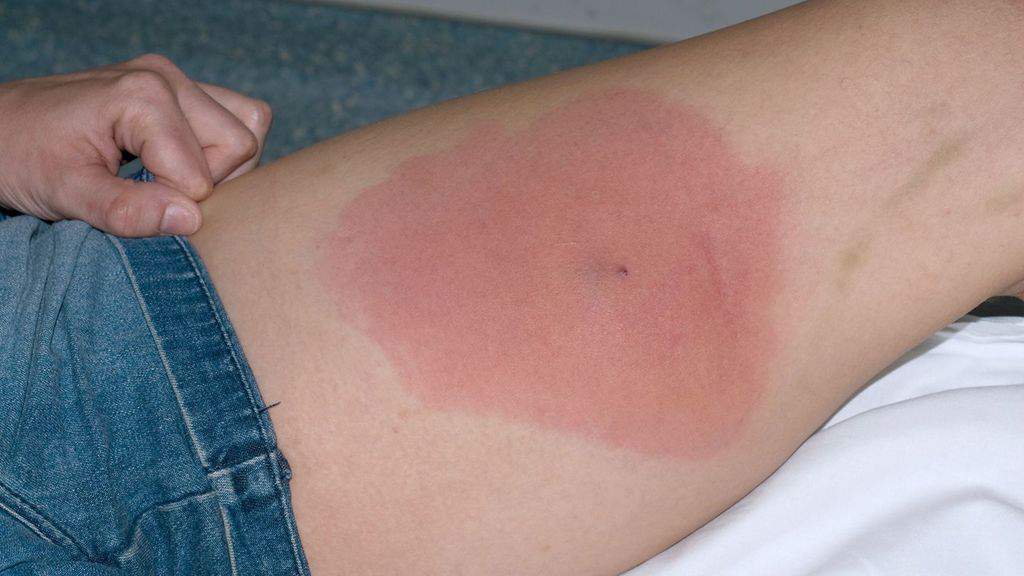
How is a MRSA Infection Diagnosed?
A sample is usually taken from the area of infection such as a skin boil and grown in the laboratory so it can be identified. If it’s a Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, it can be tested to see if it responds to commonly-used antibiotics. If not, it’s likely MRSA and will need to be treated aggressively.
In some cases, wounds infected with MRSA require surgical drainage before starting antibiotics. Anyone infected with a MRSA bacteria needs very close follow-up and, possibly, hospitalization for IV antibiotics.
- What Is Aromatherapy Vs. What Are Essential Oils?
- What is La Tomatina in Bunol, Spain Like? What to Expect at the Famous Tomato Throwing Festival
How is MRSA Treated?
Even though MRSA bacteria are resistance to most of the most commonly used antibiotics, they usually respond to an antibiotic called Vancomycin that’s given intravenously in a hospital setting.
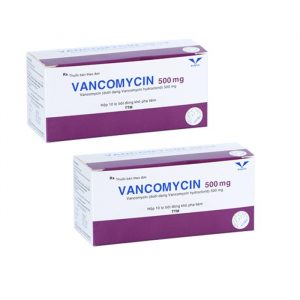
It’s important to do blood tests to check kidney function while on this antibiotic since it can damage the kidneys and hearing. Usually, IV Vancomycin is used only if the infection doesn’t get better on oral antibiotics. There are now newer antibiotics such as linezolid that can be used in severe cases of MRSA that don’t respond to vancomycin.
After a MRSA infection, it’s important to practice hand washing and good hygiene since re-infection can occur. MRSA can be successfully treated in many cases, but it can be a challenge for doctor and patient alike. This is one bacteria that definitely deserves respect.