One common way to make money on your web site is through advertising. Like a television show, ads are placed on your web site, and you are paid when visitors to your site view or interact with the ads. Sounds simple, right? Before continuing, you should make yourself familiar with some of the common terms and definitions relating to online advertising.
Advertiser / Publisher
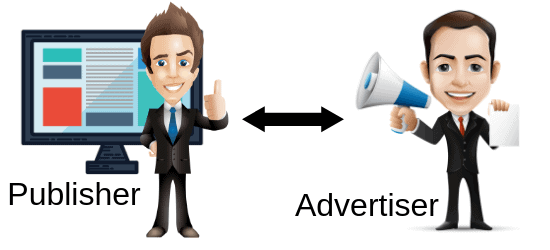
An advertiser is the person or company paying you to show the ads on your website. You are the publisher, as the one who publishes the web site and earns revenue from the ads.
CPM
Cost per thousand. CPM is an advertising rate that refers to the cost to display/show an ad to 1000 web site visitors. Payment for CPM ads is required whether the web site visitor clicks on the ad or not.
CPC
Cost per click. CPC is an advertising rate that refers to the cost to have a visitor click on an advertisement. Payment for CPC ads is required only when a user clicks on the ad, so even if your site shows the ad 1,000,000 times but has 0 clicks, you do not earn revenue.
CPA
Cost per action. Payment for CPA ads requires the web visitor to not only click on the advertisement, but they must also perform another action on the advertiser site such as make a purchase, sign up, etc.
CPL

Cost per lead. Similar to CPA, CPL requires the web visitor to click on the ad and perform an additional action on the advertiser’s site. Usually, a lead represents contact information such as an e-mail address or phone #.
Contextual ads
Contextual ads refer to ads that are displayed dynamically based on the content of the page that they are on. For example, if you own a web site about cars, the ads showing on your site would be car related.
Advertising Networks
Ad networks are companies that act as middlemen between web publishers (yourself) and advertisers. Using an ad network allows you to get big name advertisers on your site without having to work out a deal with the advertiser directly. They handle the billing and payment to you, while taking a % share of the revenue for themselves.
Inventory

Inventory refers to the number of advertisement displays you have available on your site. This is usually based on the number of visitors your site gets in a given period.
Raw vs. Unique
Raw vs. unique describes the traffic/visitors to your site. For example, say that your site gets 100 individual visitors a day. But, each visitor, visits your site 3 times a day for a total of 300 visits. You therefore have 100 unique visitors and 300 raw visitors a day. This term applies to CPM ad impressions as well. If you are being paid $5.00 CPM unique for an ad, that would be 1000 unique views, not raw.
With a basic understanding of these terms, you can feel more comfortable jumping into the online advertising world!