As a mainstream contemporary political philosophy, it worth answering the all too common question: what is Socialism? While different variants have emerged, there are a few core elements that must be noted. If one understands all main political ideologies, then he or she will be far more prepared to discover which he or she identifies with.
Socialism Defined
Socialists have very different views on the individual than their Conservative and Liberal opponents.

They do not agree with the Conservative perception of the individual as a being capable of evil, nor do they identify with the Liberal perception that individuals are self-interested. Socialism quite simply believes that the individual is a social being.
Socialists are also displeased with the capitalists system. They believe it has exploitative potential, both within developed and developing nations. Further, the competitive essence of the capitalist system threatens the very cooperative nature of humanity.

This system can cause inequalities between people within a nation because of power relations and different economic positions. They disagree with Conservatives that humans are naturally unequal, and believe inequalities are formed by this capitalist system.
To counter this system, Socialists believe that power and wealth should be redistributed to the people in an equal manner. As long as it equalizes society, the nation will become more cooperative and ensure all its people act as a unified community. Criminal activity and conflict amongst people will be reduced as equality improves, both on a human rights basis and a financial basis.

In addition to redistributing core elements of society and reducing inequalities, Socialists also want the ownership of businesses to change. Instead of privately owned businesses, Socialism wants businesses to be socially owned. If this is done, individual business owners will not be able to make the decision for the community. Instead, the community will be able to make business decisions for itself.
Utopian Socialism & Social Democracy
While the above are the core fundaments of Socialism, there are different variants that have been developed over the years. Two of the most important variants are Utopian Socialism and Social Democracy.
Utopian Socialism focuses on the public ownership of production and business, as well as public democracy.

Utopian Socialists want to establish small communities that live together in harmony; sharing all goods, owning property in a collective way, and performing work cooperatively. One of the best examples of such a community is New Harmony, which was founded within Indiana and in 1825.
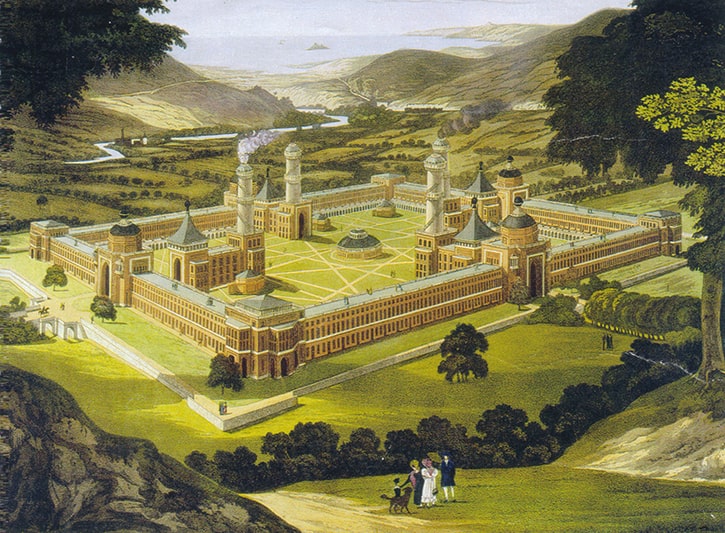
Until it lost its abilities to maintain democratic decision making and economic independence, this community flourished as one of the best examples of Utopian Socialism.
Social Democracy can largely be seen as the contemporary political philosophy variant. Those who identify with this variant call themselves Social Democrats. The believe that the social economic system is no longer an ideal choice, and would prefer to initiate reforms on the capitalists system.

Their end goal with these reforms is to develop a system that works better for every individual and levels the playing field. They hope this will create better social and economic equalities, which will lead to a great democracy.
Along these same capitalists reforms, Social Democrats want the excesses of capitalism to be used toward further developing the welfare state and increasing equality. Essentially, they want to ensure all individuals within the nation have greater access to child care, employment, health, and education.
The Socialist Objective

Clearly, if there is one dominant principle within this contemporary political philosophy, it is equality. Equality is the critical principle within Socialism. Along with Liberalism and Conservatism, this ideology is one of the mainstream political philosophies that have progressed over the ages and are still prominent within today’s society. Understanding the main elements of this ideology will help one identify with one of the three specific thoughts.